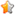|
無(wú)論使用任何語(yǔ)言做模擬登陸或者抓取訪(fǎng)問(wèn)頁(yè)面,無(wú)外乎以下思路:
觀察這三個(gè)請(qǐng)求的詳細(xì)信息,,不難看出第一個(gè)GET請(qǐng)求的地址可以由POST的響應(yīng)得到,,而第二個(gè)GET請(qǐng)求的地址又由第一個(gè)GET的響應(yīng)得到。
HttpWebRequest request = null;
HttpWebResponse response = null;
string gethost = string.Empty;
CookieContainer cc = new CookieContainer();
string Cookiesstr = string.Empty;
try
{
//第一次POST請(qǐng)求
string postdata = "email=" + UserName.Replace("@", "%40") + "&password=" + PassWord + "&origURL=" + HostUrl + "&domain=renren.com";//模擬請(qǐng)求數(shù)據(jù),,數(shù)據(jù)樣式可以用FireBug插件得到。人人網(wǎng)POST數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),,用戶(hù)名郵箱中的“@”變?yōu)椤?40”,,所以我們也要作此變化
string LoginUrl="http://www.renren.com/PLogin.do";
request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(LoginUrl);//實(shí)例化web訪(fǎng)問(wèn)類(lèi)
request.Method = "POST";//數(shù)據(jù)提交方式為POST
//模擬頭
request.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
byte[] postdatabytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(postdata);
request.ContentLength = postdatabytes.Length;
//request.Referer = "http://www.renren.com/Login.do?rf=r&domain=renren.com&origURL=" + HostUrl;
request.AllowAutoRedirect = false;
request.CookieContainer = cc;
request.KeepAlive = true;
//提交請(qǐng)求
Stream stream;
stream = request.GetRequestStream();
stream.Write(postdatabytes, 0, postdatabytes.Length);
stream.Close();
//接收響應(yīng)
response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
//保存返回cookie
response.Cookies = request.CookieContainer.GetCookies(request.RequestUri);
CookieCollection cook = response.Cookies;
string strcrook = request.CookieContainer.GetCookieHeader(request.RequestUri);
Cookiesstr = strcrook;
//取第一次GET跳轉(zhuǎn)地址
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8);
string content = sr.ReadToEnd();
response.Close();
string[] substr = content.Split(new char[] { '"' });
gethost = substr[1];
}
catch (Exception)
{
//第一次POST出錯(cuò);
}
注釋寫(xiě)的很詳細(xì)了,,在這就不再分析,,也許有人對(duì)request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(LoginUrl)有疑問(wèn),可以去google一下HttpWebRequest和WebRequest的區(qū)別,,簡(jiǎn)單來(lái)說(shuō)WebRequest是一個(gè)抽象類(lèi),,不能直接實(shí)例化,需要被繼承,,而HttpWebRequest繼承自WebRequest,。 再模擬第一個(gè)和第二個(gè)GET請(qǐng)求
try
{
request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(gethost);
request.Method = "GET";
request.KeepAlive = true;
request.Headers.Add("Cookie:" + Cookiesstr);
request.CookieContainer = cc;
request.AllowAutoRedirect = false;
response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
//設(shè)置cookie
Cookiesstr = request.CookieContainer.GetCookieHeader(request.RequestUri);
//取再次跳轉(zhuǎn)鏈接
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8);
string ss = sr.ReadToEnd();
string[] substr = ss.Split(new char[] { '"' });
gethost = substr[1];
request.Abort();
sr.Close();
response.Close();
}
catch (Exception)
{
//第一次GET出錯(cuò)
}
try
{
//第二次GET請(qǐng)求
request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(gethost);
request.Method = "GET";
request.KeepAlive = true;
request.Headers.Add("Cookie:" + Cookiesstr);
request.CookieContainer = cc;
request.AllowAutoRedirect = false;
response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
//設(shè)置cookie
Cookiesstr = request.CookieContainer.GetCookieHeader(request.RequestUri);
request.Abort();
response.Close();
}
catch (Exception)
{
//第二次GET出錯(cuò)
}
GET與POST請(qǐng)求大同小異,這里便不再累述,。三次請(qǐng)求結(jié)束,,保存好你的cookie string,每次請(qǐng)求的時(shí)候都賦給請(qǐng)求的頭部,,你就處于登錄狀態(tài)了,。 |