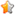1 簡介
Char-RNN,,字符級循環(huán)神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò),出自于Andrej Karpathy寫的The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks,。眾所周知,,RNN非常擅長處理序列問題。序列數(shù)據(jù)前后有很強(qiáng)的關(guān)聯(lián)性,,而RNN通過每個單元權(quán)重與偏置的共享以及循環(huán)計(jì)算(前面處理過的信息會被利用處理后續(xù)信息)來體現(xiàn),。Char-RNN模型是從字符的維度上,讓機(jī)器生成文本,,即通過已經(jīng)觀測到的字符出發(fā),,預(yù)測下一個字符出現(xiàn)的概率,也就是序列數(shù)據(jù)的推測?,F(xiàn)在網(wǎng)上介紹的用深度學(xué)習(xí)寫歌,、寫詩、寫小說的大多都是基于這個方法,。
在基本的RNN單元中,,只有一個隱藏狀態(tài),,對于長距離的記憶效果很差(序列開始的信息在后期保留很少),而且存在梯度消失的問題,,因此誕生了許多變體,,如LSTM、GRU等,。本文介紹的Char-RNN就是選用LSTM作為基本模型,。
2 Char RNN 原理

上圖展示了Char-RNN的原理。以要讓模型學(xué)習(xí)寫出“hello”為例,,Char-RNN的輸入輸出層都是以字符為單位,。輸入“h”,,應(yīng)該輸出“e”,;輸入“e”,則應(yīng)該輸出后續(xù)的“l(fā)”,。輸入層我們可以用只有一個元素為1的向量來編碼不同的字符,,例如,h被編碼為“1000”,、“e”被編碼為“0100”,,而“l(fā)”被編碼為“0010”。使用RNN的學(xué)習(xí)目標(biāo)是,,可以讓生成的下一個字符盡量與訓(xùn)練樣本里的目標(biāo)輸出一致,。在圖一的例子中,根據(jù)前兩個字符產(chǎn)生的狀態(tài)和第三個輸入“l(fā)”預(yù)測出的下一個字符的向量為<0.1, 0.5, 1.9, -1.1>,,最大的一維是第三維,,對應(yīng)的字符則為“0010”,正好是“l(fā)”,。這就是一個正確的預(yù)測,。但從第一個“h”得到的輸出向量是第四維最大,對應(yīng)的并不是“e”,,這樣就產(chǎn)生代價,。學(xué)習(xí)的過程就是不斷降低這個代價。學(xué)習(xí)到的模型,,對任何輸入字符可以很好地不斷預(yù)測下一個字符,,如此一來就能生成句子或段落。
3 實(shí)踐
下面是一個利用Char RNN實(shí)現(xiàn)寫詩的應(yīng)用,,代碼來自來自原先比較火的項(xiàng)目:https://github.com/jinfagang/tensorflow_poems,,然后自己將其做成WEB應(yīng)用,湊著學(xué)習(xí)了下如何使用tensorflow實(shí)現(xiàn)char rnn
def char_rnn(model,input_data,output_data,vocab_size,rnn_size=128,num_layers=2,batch_size=64,
learning_rate=0.01):
"""
:param model: rnn單元的類型 rnn, lstm gru
:param input_data: 輸入數(shù)據(jù)
:param output_data: 輸出數(shù)據(jù)
:param vocab_size: 詞匯大小
:param rnn_size:
:param num_layers:
:param batch_size:
:param learning_rate:學(xué)習(xí)率
:return:
"""
end_points = {}
if model=='rnn':
cell_fun=tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell
elif model=='gru':
cell_fun=tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell
elif model=='lstm':
cell_fun=tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell
cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True)
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True)
if output_data is not None:
initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32)
else:
initial_state = cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
embedding=tf.get_variable('embedding',initializer=tf.random_uniform(
[vocab_size+1,rnn_size],-1.0,1.0))
inputs=tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding,input_data)
# [batch_size, ?, rnn_size] = [64, ?, 128]
outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state)
output = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, rnn_size])
# logit計(jì)算
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([rnn_size, vocab_size + 1]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[vocab_size + 1]))
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output, weights), bias=bias)
# [?, vocab_size+1]
if output_data is not None:
# 獨(dú)熱編碼
labels = tf.one_hot(tf.reshape(output_data, [-1]), depth=vocab_size + 1)
# [?, vocab_size+1]
loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits)
# [?, vocab_size+1]
total_loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(total_loss)
end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state
end_points['output'] = output
end_points['train_op'] = train_op
end_points['total_loss'] = total_loss
end_points['loss'] = loss
end_points['last_state'] = last_state
else:
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state
end_points['last_state'] = last_state
end_points['prediction'] = prediction
return end_points效果如下:


項(xiàng)目地址:https://github.com/yanqiangmiffy/char-rnn-writer/
4 參考資料
yanqiangmiffy/char-rnn-writer: 基于Char RNN實(shí)現(xiàn)的“作家”應(yīng)用,,可以寫詩也可以寫小說,,看起來還ok
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) – Part 1: Basic RNN / Char-RNN – The Neural Perspective
Tensorflow下Char-RNN項(xiàng)目代碼詳解-學(xué)路網(wǎng)-學(xué)習(xí)路上 有我相伴
hzy46/Char-RNN-TensorFlow: Multi-language Char RNN for TensorFlow >= 1.2.
[譯] RNN 循環(huán)神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)系列 1:基本 RNN 與 CHAR-RNN-博客-云棲社區(qū)-阿里云